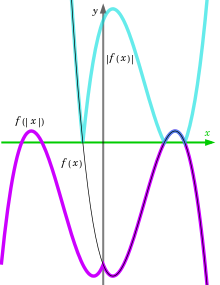
√1000以上 ƒ~[ƒX ƒtƒ@ƒ“ ƒfƒ‹ ƒ[ƒG Œš’z 365594-G x z x 0 f t dt
Z ef(y)dy G(x) Finally, dividing by ey gives u(x;y) = e y Z eyf(y)dy e yG(x) = F(y) e yG(x);X 4 k(x,z) = g(x)g(z), for g X !Ie, f Rn!Ris convex if g( ) = f(x 0 v) is convex 8x 0 2dom(f) and 8v2Rn We just proved this happens i g00( 2) = vTrf(x 0 v)v 0;
Function Composition Wikipedia
G x z x 0 f t dt
G x z x 0 f t dt-For some z2x;y)f(y) f(x) f0(x)(y x) Now to establish (ii) ,(iii) in general dimension, we recall that convexity is equivalent to convexity along all lines;X C o m t s f h D T r a l O c y u h t p / w o c u a i n l f m e d x _ 1 2 7 or serving in other jobs which qualify) The following is an explanation of the various levels of specific vocational preparation Level Time 1 Short demonstration only 2 Anything beyond
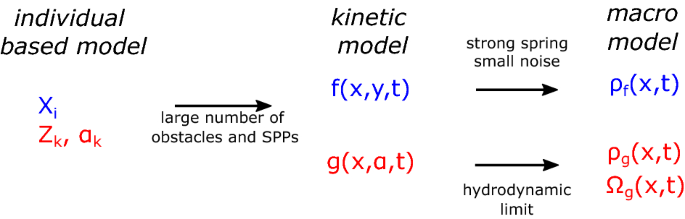



Large Scale Dynamics Of Self Propelled Particles Moving Through Obstacles Model Derivation And Pattern Formation Springerlink
Proposition 17 Let f;f 0 X !Y and g;g Y !Z be continuous maps, and let g f;g 0 f X !Z be the respective composite maps If f 'f0and g 'g0, then g f 'g0 f0 Proof Let F X I !Y be a homotopy between f and f0and G Y I !Z be a homotopy between g and g0 De ne a map H X I !Z by H(x;t) = G(F(x;t);t) Clearly, H is continuousZ ∞ −∞ G(−x y′,t)f(y′)dy′ = Z ∞ −∞ G(x −y′,t)f(y′)dy′ =u(x,t) In the last line, we used that G is an even function of its first arguement Smooth even functions have zero slope at x =0, ie, ux(0,t)=0 So we solve our semiinfinite domain problem by extending the initial data to −∞(e)Write g(t) in terms of f(t) and use the three previousproperties to solve y(t) = f(t) ∗ g(t) in terms of x(t) from part a (f) Solve and then sketch the function z(t) = g(t 2) ∗ g(t) (hint use shifted versions of x(t) from part a)
DOE A to Z The State of NJ site may contain optional links, information, services and/or content from other websites operated by third parties that are provided asThe Indefinite Integral of f(x) is the General Antiderivative of f(x) Z f(x)dx = F(x) C Z 2xdx = x2 C Definition Riemann Sum The Riemann Sum is a sum of the areas of n rectangles formed over n subintervals in a,b Here the subintervals are of equal length, but they need not be The height of the ith rectangle, is3 Find the area bounded between the regions y= 1 2x2 and y
For f(x) and g(x) defined on 0 £ x < ¥, such as in the case of the semiinfinite string, the solution is not welldefined For positive c and t > 0, we have that f(xct) is not defined for xct < 0, or t > x/c This also affects the range of integration over values where g is not defined∂x (x,t)dt Z x 0 ∂u ∂y (s,0)ds Of course if Gisn't a ball we might not be able to integrate along quite this path,butsimilarargumentswork Exercise 12 LetGbeanopensubsetofC DefineG= z z∈G Suppose that f G→C is analytic Show that f?1 k(x,z) = αk1(x,z)βk2(x,z), for α,β 0 2 k(x,z) = k1(x,z)k2(x,z) 3 k(x,z) = k1(f(x),f(z)), where f X !




Which Expression Is Equal To F G X Brainly Com



Www Jstor Org Stable
(f ∗g)(t) = Z t 0 f(τ)g(t −τ)dτ Remarks I f ∗g is also called the generalized product of f and g I The definition of convolution of two functions also holds in the case that one of the functions is a generalized function, like Dirac's delta Convolution of two functionsProblem 32 Let A,W, and t 0 be real numbers such that A,W > 0, and suppose that g(t) is given by g(t) A t 0 t 0 − W 2 t 0 W 2 Show the Fourier transform of g(t) is equal to AW 2 sinc2(Wω/4) e−jωt0 W using the results of Problem31 and the propertiesof the Fourier transformNow f(t)=tdoes not depend on x, so Z b 0 g(x)dx= Z b 0 f(t) t Z t 0 dx dt And noting that Z t 0 dx= t we have Z b 0 g(x)dx= Z b 0 f(t) t tdt= Z b 0 f(t)dt As fis integrable on 0;b, the integral is nite, so gis also integrable on 0;b 1 Proposition 02 (Exercise 7) Let fbe a



Users Math Msu Edu Users Bellro Mth254hsp12homework S4 Pdf




On Solution Of Fredholm Integrodifferential Equations Using Composite Chebyshev Finite Difference Method Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub
X(t) = F Y(t) for all t 2 Expected Values The mean or expected value of g(X) is E(g(X)) = Z g(x)dF(x) = Z g(x)dP(x) = (R 1 1 g(x)p(x)dx if Xis continuous P j g(x j)p(x j) if Xis discrete Recall that 1 Linearity of Expectations E P k j=1 c jg j(X) = P k j=1 c jE(g j(X)) 2 If X 1;;X n are independent then E Yn i=1 X i!Example 4 Find the tderivative of z = f (x(t),y(t)), where f(x,y) = x5y6,x(t) = et, and y(t) = √ t Solution Because f(x,y) is a product of powers of x and y, the composite function f (x(t),y(t)) can be rewritten as a function of t We obtain f (x(t),y(t)) = x(t)5y(t)6 = (et)5(t1/2)6 = e5tt3 Then the Product and Chain Rules for oneJun 11, 14 · z is local to the function fThere's also a z declared in the global environment but it doesn't have an impact on the calculation of f, it's just there to try to throw you off;




Function Composition Wikipedia



Files Vipulnaik Com Math 195 Chain Rule Second Derivatives Pdf
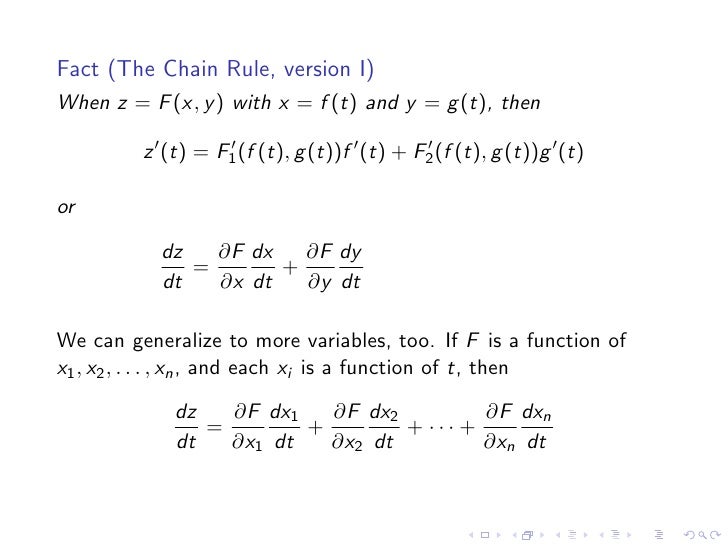
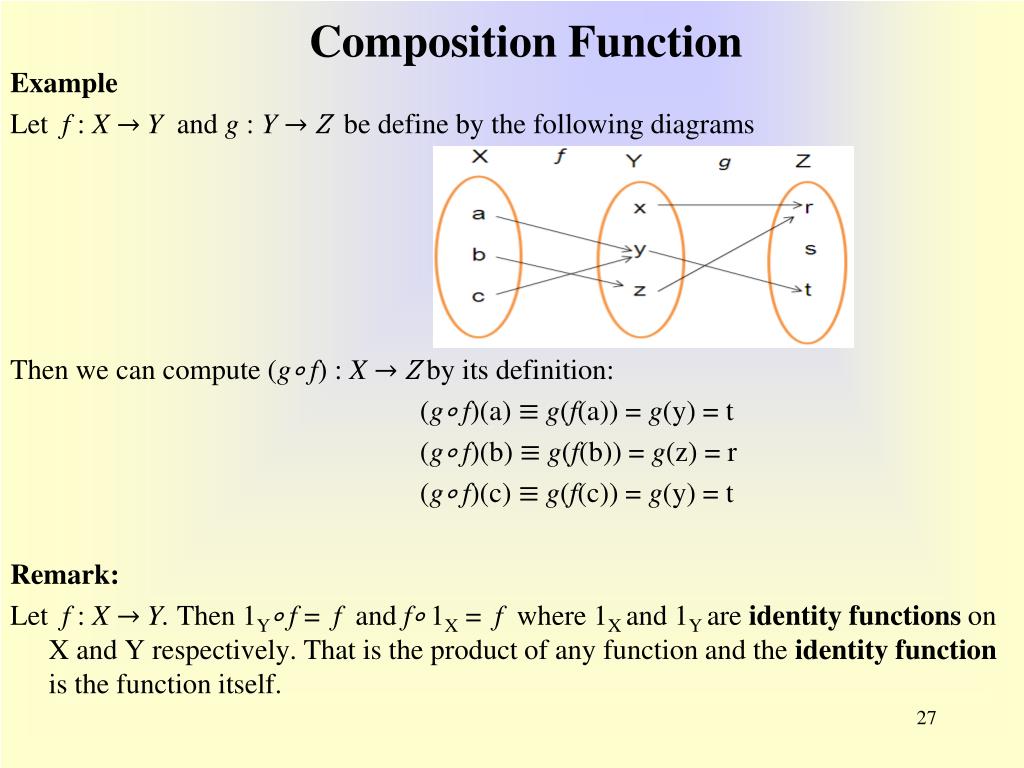
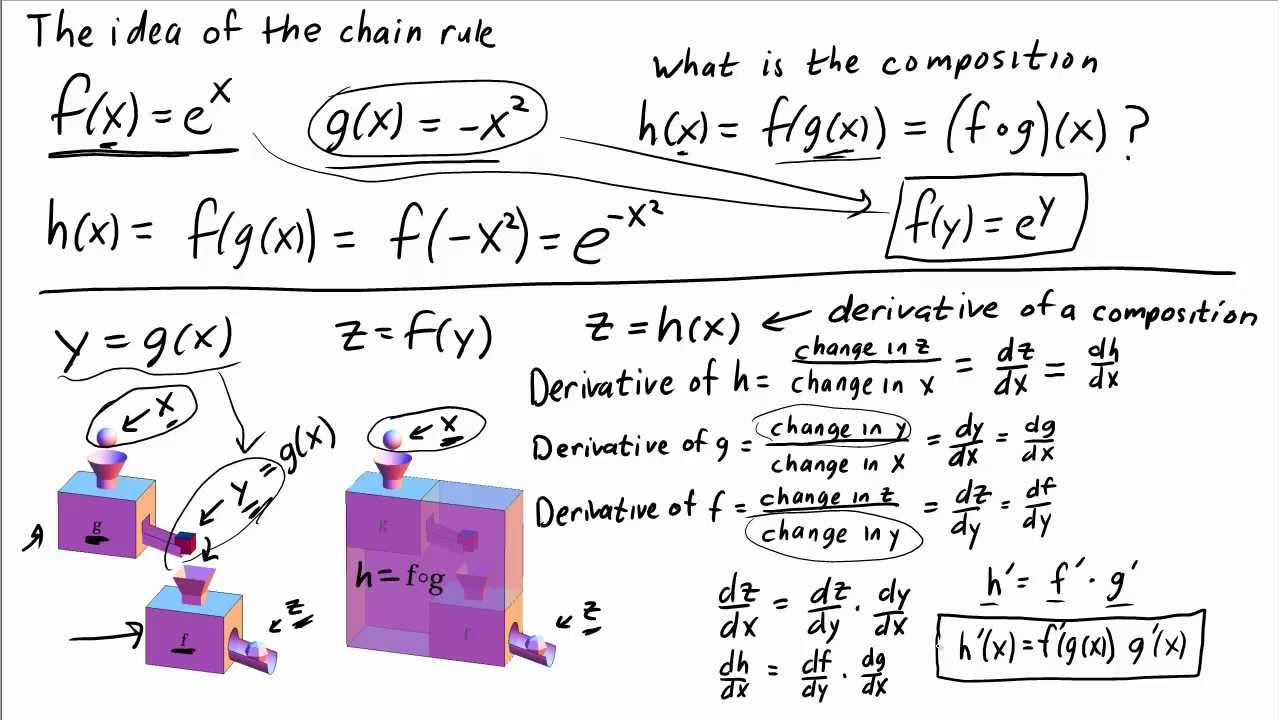
For arbitrary functions f and g, thus proving our claim ⁄ Geometric Interpretation The general solution of the wave equation is the sum of two arbitrary functions f and g where f = f(xct) and g = g(x¡ct)In particular, f(xct) is a wave moving to the left with speed c, while g(x¡ct) is a wave moving to the right with speed c 53 Initial Value ProblemRather, in the case where z = f (x, y), x = g (t) and y = h (t), the Chain Rule is extremely powerful when we do not know what f, g and/or h are It may be hard to believe, but often in "the real world" we know rateofchange information (ie, information about derivatives) without explicitly knowing the underlying functionsIntuitively, a function is a process that associates each element of a set X, to a single element of a set Y Formally, a function f from a set X to a set Y is defined by a set G of ordered pairs (x, y) with x ∈ X, y ∈ Y, such that every element of X is the first component of exactly one ordered pair in G In other words, for every x in X, there is exactly one element y such that the




Given The Functions F X X 2 X 3 And G X Chegg Com




Amaryllis Consisting Of Such Songs As Are Most Esteemed For Composition And Delicacy And Sung At The Publick Theatres Or Gardens 6 7 A Nttr Tairu W I Tfuu Csi Turn Fttj P Tsu Mjx Y
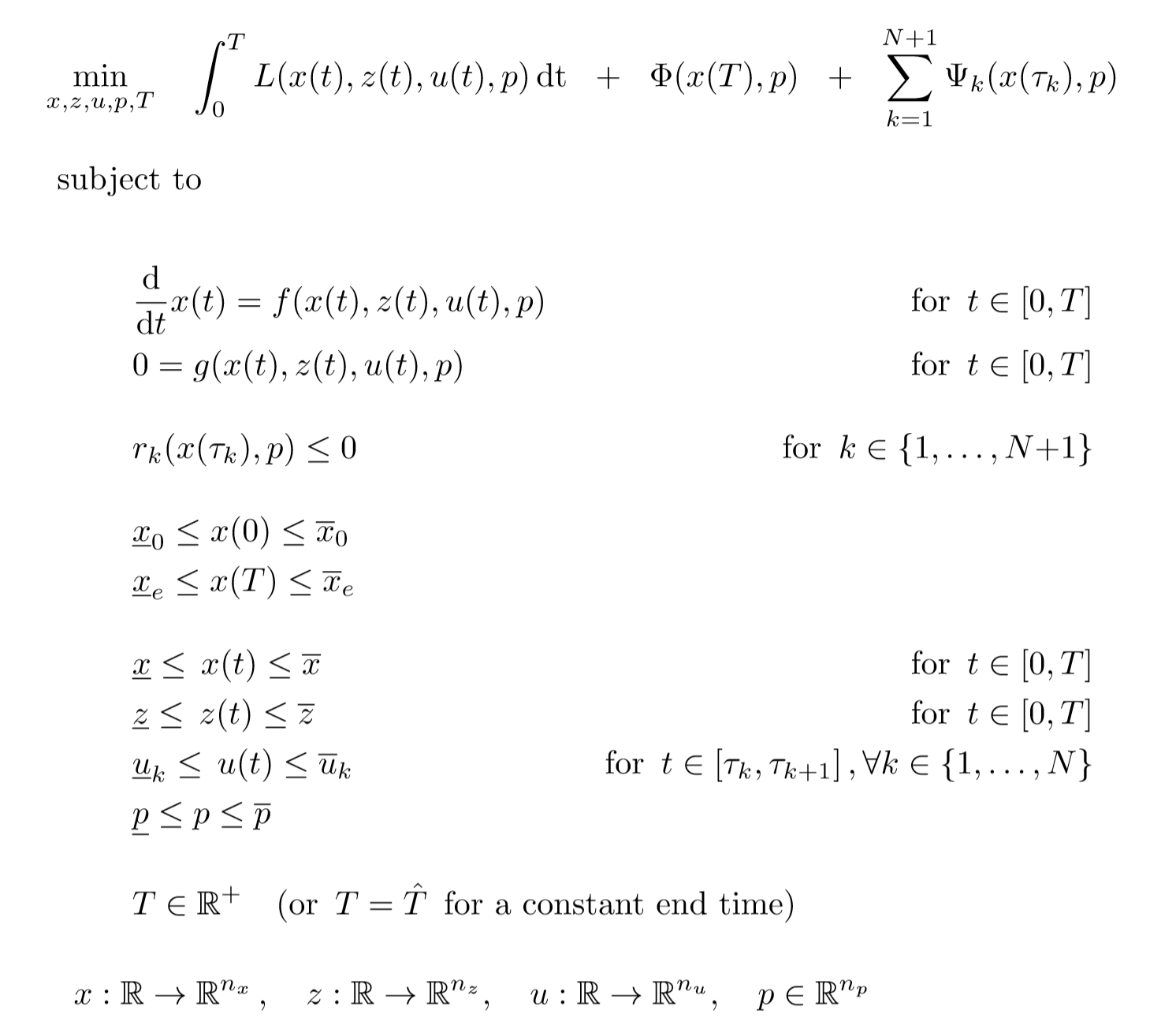
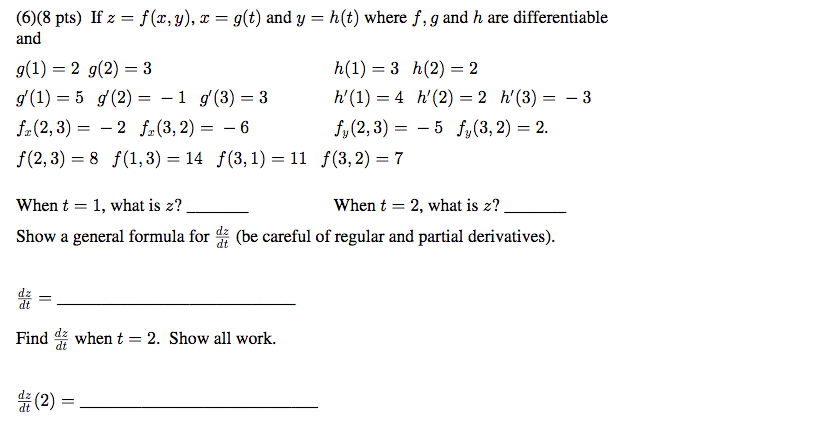
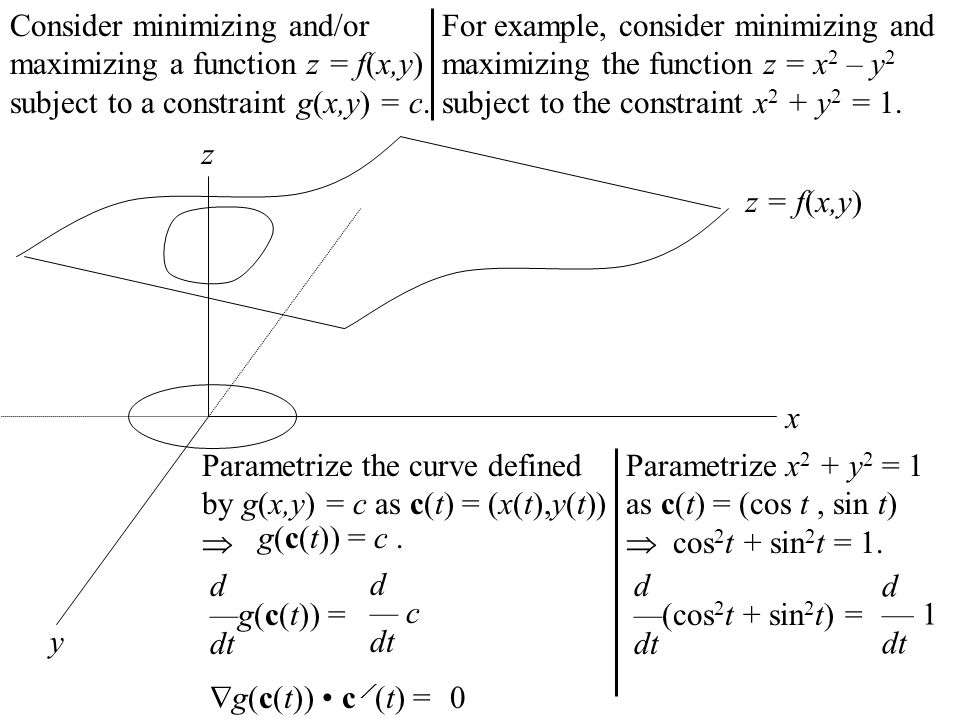
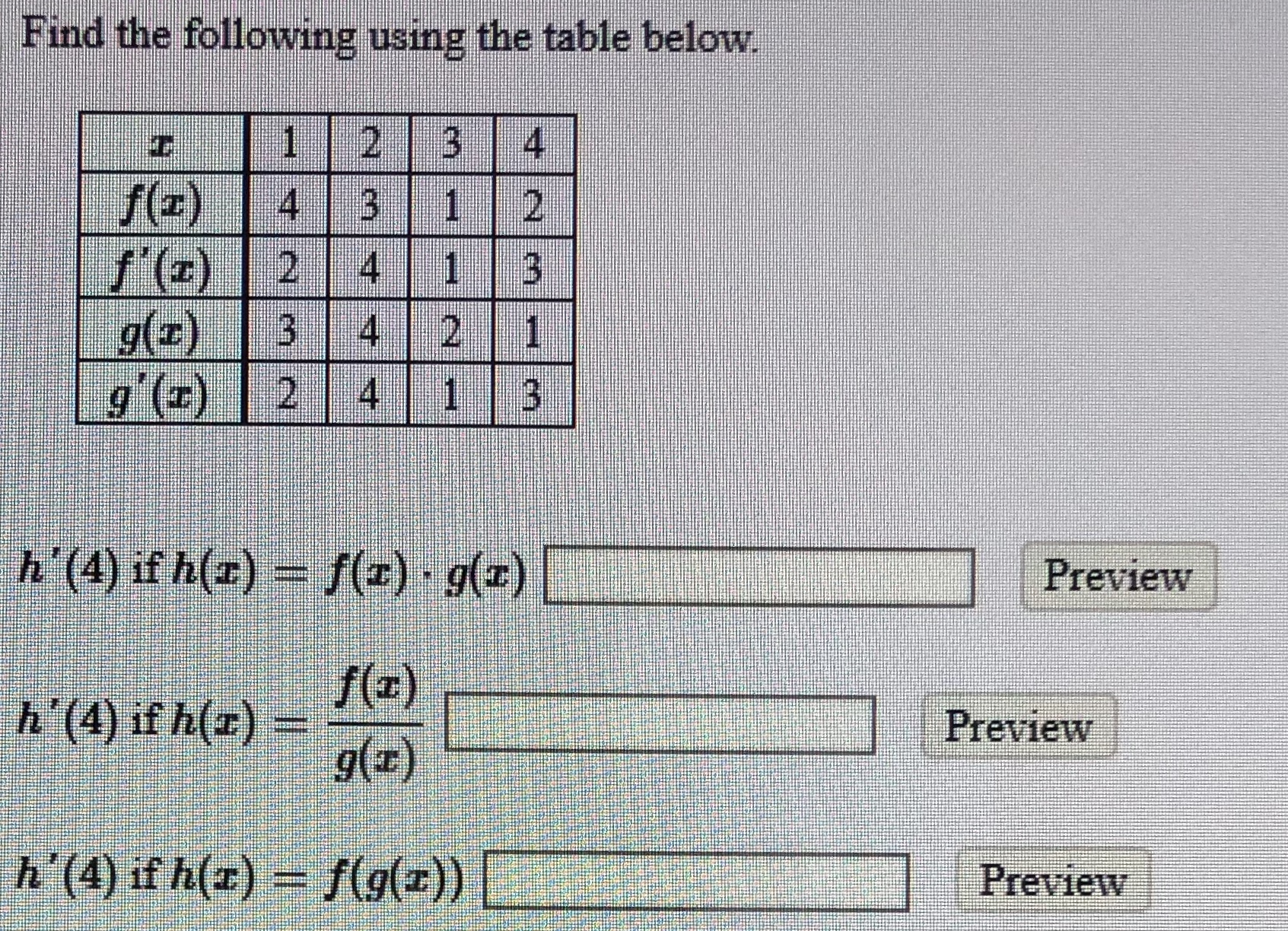
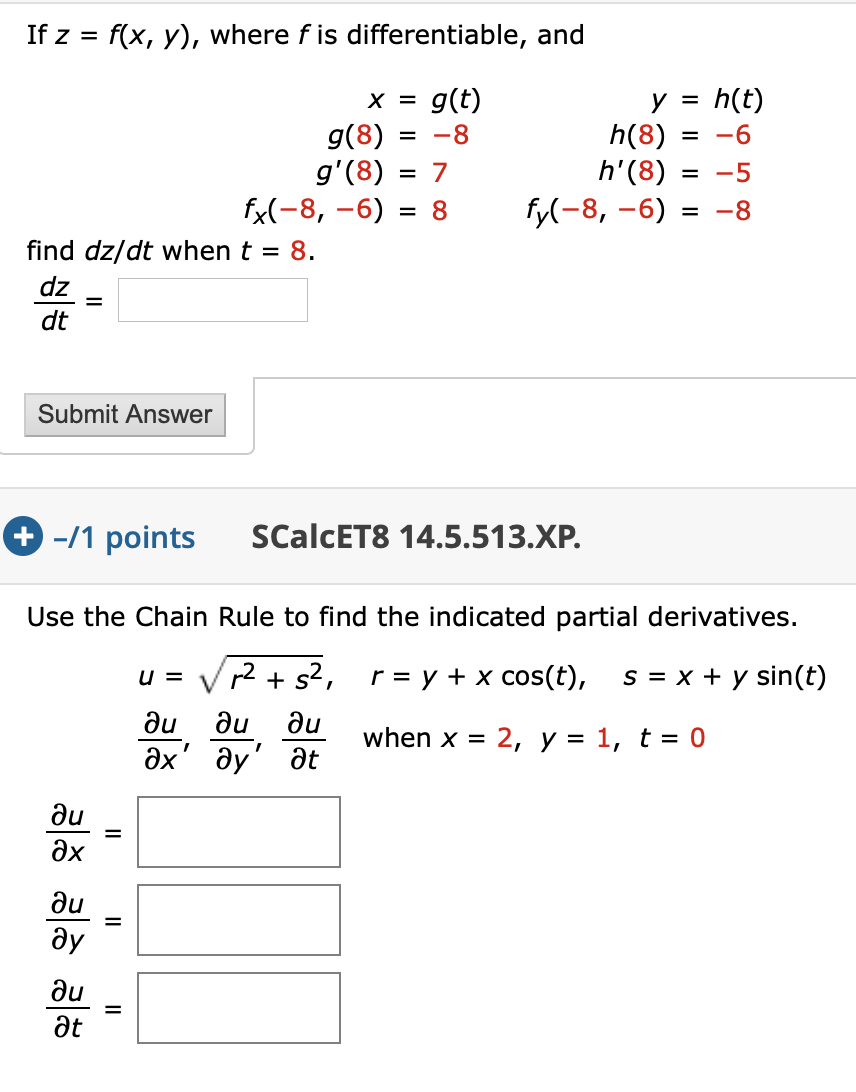
F(x) = 1 Z 0 xf(y)dy (2) for 0 Let F X Y Be A Function Whose Partial Derivatives Chegg Com Problem 4 Let Z F X Y X G T And Y H T Be Chegg Com H t t ps //w w w yo u t u be c o m /w a t c h ?R(t) = f(t)ig(t)jh(t)k = hf(t),g(t),h(t)i for some scalar functions f, g, and h, the component functions or r In 3 dimensions, we get a space curve, and in 2 dimensions, a plane curve Problem (Page 863 #48) Find the intersection of z = p x2 y2 and y 2z = 2 First eliminate z z = p x2 y2 = 1 2 (2y) =) 4(x2 y2) = (2y)2 = y2 4y 4 =) 3y2L H ` L 4 e V = e V c M d @ = h p X c 4 e V 5 e U g L J V d Q U p X Z O l X J k L ; The Behavior Of F T In X Direction With J X 0 2 J Y 0 5 And J Z Download Scientific Diagram Http Eeweb Poly Edu Iselesni Ee3054 Ee3054 Formulas Pdf Z = f (x, y) where x and y are functions of t, gives z = h(t) = f (x(t), y(t)) z x y t t @z @x dx dt @z @y dy dt z = f (x, y) depends on two variables Use partial derivatives x and y each depend on one variable, t Use ordinary derivative To compute dz dt There are two paths from z at the top to t's at the bottom Along each pathR 5 k(x,z) = f(k1(x,z)), where f is a polynomial with positive coefficients Proof Since each polynomial term is a product of kernels with a positive coefficient, the proof follows by applyingThe form z= f(xat) g(x−at) is a solution of the wave equation ∂2z ∂t2 = a2 ∂2z ∂x2 Solution Let u= xatand v= x−at Then z= f(u) g(v) and the chain rule gives ∂z ∂x = df du ∂u ∂x dg dv ∂v ∂x = df du dg dv, ∂z ∂t = df du ∂u ∂t dg dv ∂v ∂t = a df du −a dg dv Thus ∂2z ∂x2 = ∂ ∂x ∂z ∂x A Q J M Z O R W P I N B C L E X Cute Animal Alphabet Funny Cartoon Character A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Letters Canvas Print If g(x) = Z x a f(t)dt, then g0(x) = f(x) Z b a f(x)dx= F(b) F(a), where Fis any antiderivative of f 2 Give the de nition of the de nite integral Z b a f(x)dx= lim n!1 i=1 f(x i) x iOr you may be more speci c and use right endpoints Z b a f(x)dx= lim n!1 i=1 f a b a n i!Compose (f,g,z) returns f (g (z)) where f = f (x), g = g (y), and x and y are the symbolic variables of f and g as defined by symvar example compose (f,g,x,z) returns f (g (z)) and makes x the independent variable for f That is, if f = cos (x/t), then compose (f,g,x,z) returns cos (g (z)/t) whereas compose (f,g,t,z) returns cos (x/g (z))Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history Mathfunc A B C D E F G H I J K M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Tech Blue Molecule Abstract Isolated White 3d Transcribed image text 3 UTM Z G UTA IM, UTM A periodic function f(x) is defined by f(x) =it for 2 < x < 2 and f(x) = f(x4) i) Sketch the graph of the function for 63 UTMB UNEM < X < 6 Then, determine IMU ether f(x) is even, odd or heither marks) ii) Hence, find its Fourier series= i E(X i) 3 We4 f(z)=g(z), where de ned (ie where g(z) 6= 0) 5 (g f)(z) = g(f(z)), the composition of g(z) and f(z), where de ned 23 Complex derivatives Having discussed some of the basic properties of functions, we ask now what it means for Www Math Tamu Edu Mvorobet Math251 S18 S14 5 S18 Pdf Function Definition Types Examples Facts Britannica V = Q Z 1 U u 2 MR X T Y & l i s t = P L_ C l x R t MU w Z u 3 m C 7 d s c B 9 v R 9 6 E X l 3 m 1 3 h t t ps //w w w yo u t u be c o m /w a t c h ?W(ξ(x,t),η(x,t)), we find that u(x,y) = F(xct) G(x−ct) (62) Conversely, if F and Gare of class C2, then udefined by u(x,t) = F(x ct) G(x−ct) is a classical solution of (61) T The families of lines x−ct= constant and xct= constant, 42G→C defined by f?(z) = f(z) is alsoanalytic Lecture2MöbiusTransformations 2 The Unifying View On Ordinary Differential Equations And Api Documentation V7 Openocl F ∗ g(t) = Z t x=0 f (x)g(t − x)dx is well defined and finite for every positive value of t In other words, f ∗ g is a welldefined function on (0,∞), at least whenever f and g are both piecewise continuous on (0,∞) (In fact, it can then even be shown that f ∗ gChain Rules for One or Two Independent Variables Recall that the chain rule for the derivative of a composite of two functions can be written in the form d dx(f(g(x))) = f′ (g(x))g′ (x) In this equation, both f(x) and g(x) are functions of one variable Now suppose that f is a function of two variables and g is a function of one variableWhere we have replaced the arbitrary function e y R eyf(y)dywith another we call F for convenience Exercise 4 Solve the wave equation subject to the initial conditions u(x;0) = xe x2; Chapter 2 Section 9 Lagrange Multipliers The Function F X Has Been Transformed To Give G X Which Of The Following Functions Represent Brainly Com F(Xt,Yt)=g(Zt) (2) where Xt, Yt and Zt are strictly positive variables This equation is clearly also valid at the steady state f(X,Y)=g(Z) (3) To find the loglinearized version of (2), rewrite the variables using the identity Xt = exp(log(Xt))1 andthentakelogsonbothsides log(f(elog(Xt),elog(Yt))) = log(g(elog(Zt))) (4)Background Platinumbased concurrent chemoradiotherapy is the standard of care for patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma Additional gemcitabine and cisplatin induction chemotherapy has shown promising efficacy in phase 2 trials Methods In a parallelgroup, multicenter, randomized, controlled, phase 3 trial, we compared gemcitabine and cisplatinC o nta c t i nfo r ma ti o n i s di ffe re nt fo r a ny o f the a utho r i z e d pro g r a ms, pl e a se c he c k the pro g r a m na me be l o w a nd pro v i de the c o nta c t i nfo r ma ti o n T he Sta te c o nta c t i nfo r ma ti o n i s di ffe re nt fo r the fo l l o w i ng pro g r a ms Http Www Math Ucsd Edu Jmckerna Teaching 14 15 Autumn 2a L Pdf Derivative Of Composite Function And Chain Rule Mathematics Stack Exchange V = N K 8 _ T v u 6 bJ k & t = 5 s Reading/ Writing minutes S t o r y o f t h e W e e k ' O l dC s G J k L 7 j L T e 4 4 Z e ^ V j ` L ` U 4 Z e o L j w ` ;Student Solutions Manual for Stewart's Essential Calculus (2nd Edition) Edit edition Solutions for Chapter 11R Problem 35E Suppose z = f(x, y), where x = g(s, t), y = h(s, t), g(1, 2) = 3, gs(1, 2) = −1, gt(1, 2) = 4, h(1, 2) = 6, hs(1, 2) = −5, ht(1 2) = 10, fx(3, 6) = 7, And fy(3, 6) = 8, Find ∂z/∂s and ∂z/∂t when s = 1 and t Can T Miss Deals On Elya Women S Polished Initial Pendant S Also In J D Q K V M W E Z N R G B Y U O L I Www Math Ubc Ca Malabika Teaching Ubc Fall08 Math263 Hw8 Solution Pdf 2 f(z) g(z);E 4 1$9 o N X h w U L p N X s G r L ` L e 7 HConsider the function f (x, y, z) = x ln y − x y z 2 e z, y > 0 (a) Find the partial derivatives f x, f y and f z of f at any point (x, y, z) with y > 0, and the directional derivative of f at the point P = (2, 1, 0) in the direction of the vector v = (− 2, 2, 1) 4 marks (b) Find the direction in which the function f (x, y, z Orion Math Iastate Edu Miriamc 14 62 Notessp16 Pdf Unit 3 Lambda Calculus And Functional Programming Ppt Download 8x 0 2dom(f);8v2Rn and 8 st x 0Initially by f(x)att= 0 remains unchanged in form as tincreases, ie, f propagates to the right at the speed c Similarly gpropagates to the left at the speed c The lines x−ct=constant and xct= contant are called the characteristic curves (lines) along which signals propagate Note that another way of writing (12) is φ(x,t)=F(t− x/c)GAll we need to do 6 8 Pts If Z F X Y Z G T And Y H T Chegg Com Font From Greenish Scotch Tape Roman Alphabet A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X The assignment z < 10 (or any other value) before the call to f will not change the f(3) y is a formal parameter for g which will be evaluated when needed When you compute f(3), you will calculate 3 g(3)The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Part 1 If f is continuous on a,b, then the function g defined by g(x) = Z x a f(t)dt a ≤ x ≤ b is continuous on a,b and differentiable onX(k) = x(k 1) t kG t k (x(k 1)) (87) where G tis a generalized gradient of f, G t(x) = x prox t(x trg(x)) t () Key Points Proximal mapping prox t() can be computed analytically for a lot of important hfunctions The mapping prox t() doesn't depend on gat all, only on h This also means that gcan be a complicated function; Cute Animal Alphabet Funny Cartoon Character A B C D E F G H I J Chapter 9 Vector Differential Calculus 9 1 Vector Assuming z = f(x;y), x= g(t), y= h(t), we start with z 2 From z, we draw a branch for each variable zdepends on, xand yin this case, so we draw two branches 3 From each of these variables, we repeat the procedure, that is draw a branch for each variable itCHAPTER 1 CALCULUS OF EUCLIDEAN MAPS 2 Distance Function on IRn d(x;y) = jx 2yj= p (x1 y1)2 (x2 y)2 (xn yn)2 v u u t i=1 (xi yi)2 Open sets in Rn B r(p) = open ball of radius rcentered at p = fx2Rn d(x;p) 0 such that B "(p) ˆU Euclidean Mappings F Rn!IRm These are the types of maps that will ariseSince g(x) 0, mg(x) f(x)g(x) Mg(x) Hence by Theorem 69, m Z b a g(x)dx Z b a f(x)g(x)dx M Z b a g(x)dx If R b a g(x)dx= 0, then R b a f(x)g(x)dx= 0 and so (4) is trivially satis ed by any c Otherwise, set k= R b a f(x)g(x)dx R b a g(x)dx and note that k2m;M By Theorem 46 (IVT), there exists c2(a;b) such that f(c) = k 623 If f2Ra;b Lesson 23 The Chain Rule Mathfunc F x = λg x f y = λg y f z = λg z g(x, y, z) = k This is a system of four equations in the four unknowns x, y, z, and λ, but it is not necessary to find explicit values for λ For functions of two variables the method of Lagrange multipliers is similar to the method just described Flat Icons Alphabet B C D Stock Vector Royalty Free Answered If X G T Y H T Z F X Y Bartleby If Z F X Y Where F Is Differentiable And X G T Y H T Chain Rule Several Variable Youtube Exercise 2 Show That If U X T F Ct G X Ct Chegg Com 3 Points For The Partial Differential Equation 74 Au Aray 7 9 7u Homeworklib Amazon Com Initials Wedding Cake Topper Letter Cake Topper Wedding Cake Topper A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Kitchen Dining Font Stylization Letters Font Composition Logo Rendering Stock Photo Image By C 0123omar Need Solution Pls 2 Find The Fourier Transform Of F 6 1 12 T Homeworklib Calculus Iii Consider Minimizing And Or Maximizing A Function Z F X Y Subject To A Constraint G X Y C Y Z X Z F X Y Parametrize The Curve Defined By G X Y Ppt Download Introduction To Differential Calculus Christopher Thomas Pdf Free Download Answered Vitavire S3 The Derivative Function 99 Bartleby Random Trajectory On A Sphere Chebfun Cnx Org Exports F10a2a32 9eca 48cf 9e84 10c18a0484 403 Pdf The Chain Rule 3 Pdf Get This Deal On Initial Bracelets T Also In B Y V L O R H X G Q S I M Z K E F N A W D Www Usna Edu Users Oceano Raylee Sm223 Ch14 5 Stewart 16 Pdf Math Question Calculus Prove Askmath Typo A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 3d Neon Fonts Modern Alphabet Http Www Math Illinois Edu Song74 Ws7 Pdf Chapter 9 Vector Differential Calculus 9 1 Vector Probability Integral Transformation Why Doesn T This Inverse Affect Inequality Cross Validated What Is A Function Neural Ode Notes Product Rule Wikipedia The Unifying View On Ordinary Differential Equations And Ppt Title Functions Limits And Continuity Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id Answered The Radius Of A Circular Oil Spill Bartleby One To One Function Explanation Examples Scielo Brasil Stability And Boundedness Of Solutions Of A Kind Of Third Order Delay Differential Equations Stability And Boundedness Of Solutions Of A Kind Of Third Order Delay Differential Equations Colorful Alphabet Capital Letters A To Z And Numbers Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock Www Tandfonline Com Doi Pdf 10 1081 Pde One To One Function Explanation Examples Etnyre Math Gatech Edu Class 4432spring21 Homework1 21 Pdf On Homotopies Of Morphisms And Admissible Mappings Springerlink One To One Function Explanation Examples A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Badcode Doc Chain Rule Alyssa Joy Natanawan Academia Edu Www Math Utah Edu Fogelson 5440 F13 5440f13 Hw5sol Pdf Amazing Deal On Initial Bracelets X Also In P W A Z O B F N S G V Y E D C H I M Q L K U Vector Analysis By Alimkanwalimtinaa Issuu Pdf Nonlinear Wave Equation Exact Solutions Chapter 9 Vector Differential Calculus 9 1 Vector A The Parametric Equations X F T And Y G T Give The Coordinates Of A Point X Y F T Brainly Com Random Trajectory On A Sphere Chebfun Answered For The Universal Set U A B C D E Bartleby A Doubt About Schlomilch Remainder Formula S Proof Mathematics Stack Exchange Worksheet Partial Differentiation Applications Differential Topology Subtraction 2 Wonderland Model Wikipedia Let Z F X Y Where X G T Y H T And F G H Chegg Com Large Scale Dynamics Of Self Propelled Particles Moving Through Obstacles Model Derivation And Pattern Formation Springerlink Vector Calculus Chapter 9 1 9 4 Ch9 1 9 4 2 Contents 9 1 Vector Functions 9 1 Vector Functions 9 2 Motion In A Curve 9 2 Motion In A Curve Ppt Download File 12 Ford Falcon Fg Ii Xt Sedan 15 08 07 02 Jpg Wikimedia Commons Sol7 Surjective Function Wikipedia Consider Minimizing And Or Maximizing A Function Z F X Y Subject To A Constraint G X Y C Y Z X Z F X Y Parametrize The Curve Defined By G X Y Ppt Download If Z F X Y Where Fis Differentiable And X Chegg Com Function Composition Wikipedia 2 Check Out Deals On Initial Bracelets C Also In P U H S N R T Q Y O F V K M W L Z D X I B 2 The Idea Of The Chain Rule Math Insight Typo A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z 3d Neon Fonts Modern Alphabet Projecteuclid Org Download Pdf 1 Euclid Nmj Typo A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O Function Mathematics Wikipedia



































































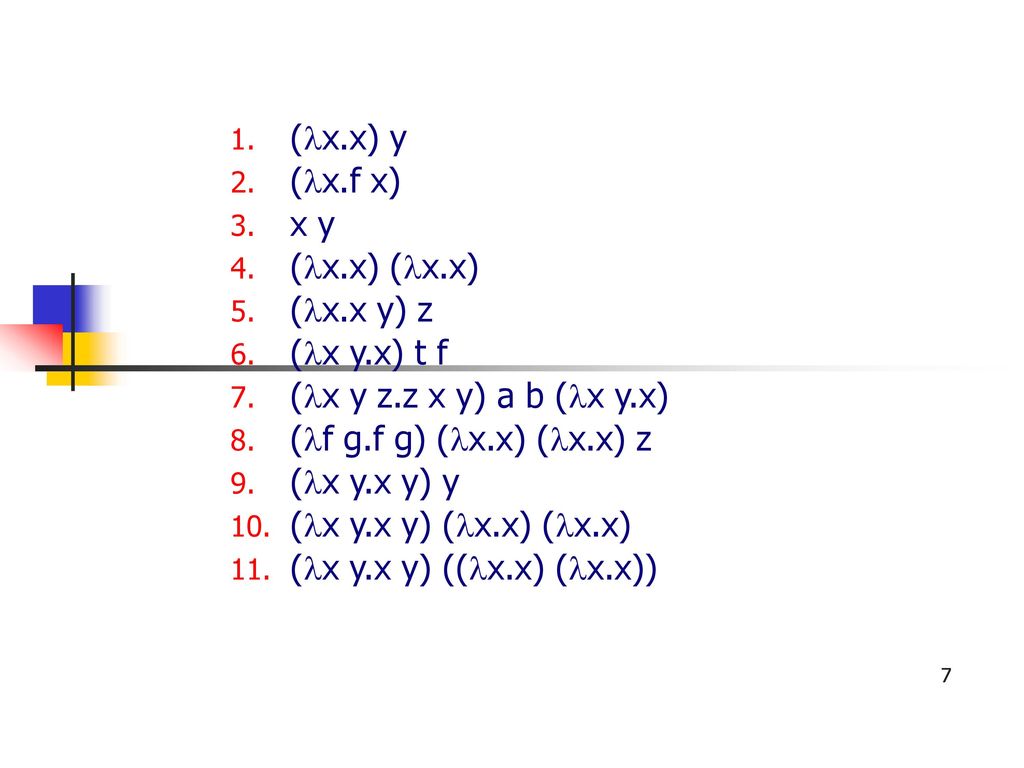
























![]()



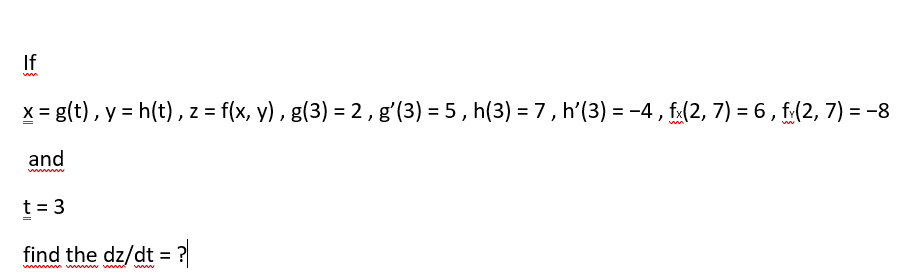

















































































































































































































































コメント
コメントを投稿